Hi Guys, in this post I will be explaining how to create a simple WCF service and host it as a 'Windows Service'.
Lets create a simple Windows Service which has a OperationContract which will add numbers and return it
Step 1: Create a simple WCF service library
Step 2: Create a simple Windows Services in which you will host the service
Step 3: Install the Windows Service
Step 4: Consume the Windows Services in a Windows Form Client.
Step 1: Create simple WCF Service library:
1. Open Visual Studio 2010 , Create new project and choose Windows Service Library named as Wcf_WindowsService_Add
2. Delete these files: App.config, IService1.cs, Service1.cs, and create your own WCF Service, Right click your project and create new item - > WCF Service name it as WindowsServiceAdd.cs
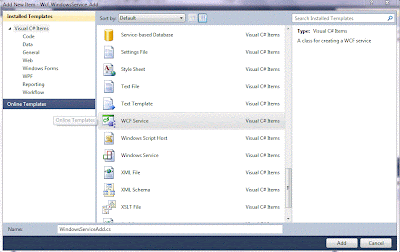
3. In app.config files you can see two endpoints with bindings wsHttpBinding and mexHttpBinding and with abase address
4. Open IWindowsServiceAdd.cs Interface remove Dowork() Contract and your Contract with name Add()
5. Open WindowsServiceAdd.cs remove DoWork() and define your Add() OperationContract :
6. Build your project , now your WCF Service library dll is ready to use.
Step 2: Create a simple Windows Services in which you will host the service:
1. Right Click your solution and create new project. -> Windows -> Windows Services.
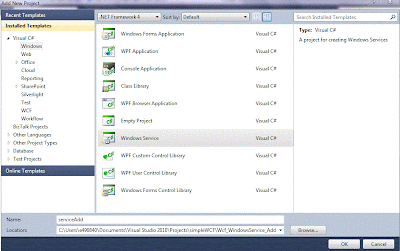
2. Delete Program.cs and Service1.cs and create your own Service , by right clicking the project add new item -> Windows Service

3. Click 'click here to switch to code view' , and modify the code as shown below to add a Service Host and methods to stop and start the services ,and add System.ServiceModel to your project , and your Service Library dll too
4. Add Program.cs file
5.Build this project . now it is ready to be installed in your machine
Step 3: Install the Windows Service
1. Inorder to install the service we need Installer class, so add new installer class:
2.Goto Start - > All programs -> Visual Studio 2010 - > Visual Studio Tools -> Visual Studio command prompt. Goto to path of your serviceAdd.exe , and install it using ' installutil serviceAdd.exe
3. You can see your service in Service Console
Step 4: Consume the Windows Services in a Windows Form Client.
1. Start your service , Create a new Windows Form project, refer your WCF hosted as Windows services ( http://localhost:8732/Design_Time_Addresses/Wcf_WindowsService_Add/WindowsServiceAdd/ ) to this project. add a lable and a button, double click the button and and add the bellow code , and run your project :
2. Build and Run your Windows Form to consume the service
Lets create a simple Windows Service which has a OperationContract which will add numbers and return it
Step 1: Create a simple WCF service library
Step 2: Create a simple Windows Services in which you will host the service
Step 3: Install the Windows Service
Step 4: Consume the Windows Services in a Windows Form Client.
Step 1: Create simple WCF Service library:
1. Open Visual Studio 2010 , Create new project and choose Windows Service Library named as Wcf_WindowsService_Add

3. In app.config files you can see two endpoints with bindings wsHttpBinding and mexHttpBinding and with abase address
4. Open IWindowsServiceAdd.cs Interface remove Dowork() Contract and your Contract with name Add()
5. Open WindowsServiceAdd.cs remove DoWork() and define your Add() OperationContract :
6. Build your project , now your WCF Service library dll is ready to use.
Step 2: Create a simple Windows Services in which you will host the service:
1. Right Click your solution and create new project. -> Windows -> Windows Services.

2. Delete Program.cs and Service1.cs and create your own Service , by right clicking the project add new item -> Windows Service

3. Click 'click here to switch to code view' , and modify the code as shown below to add a Service Host and methods to stop and start the services ,and add System.ServiceModel to your project , and your Service Library dll too
4. Add Program.cs file
5.Build this project . now it is ready to be installed in your machine
1. Inorder to install the service we need Installer class, so add new installer class:
2.Goto Start - > All programs -> Visual Studio 2010 - > Visual Studio Tools -> Visual Studio command prompt. Goto to path of your serviceAdd.exe , and install it using ' installutil serviceAdd.exe
Step 4: Consume the Windows Services in a Windows Form Client.
1. Start your service , Create a new Windows Form project, refer your WCF hosted as Windows services ( http://localhost:8732/Design_Time_Addresses/Wcf_WindowsService_Add/WindowsServiceAdd/ ) to this project. add a lable and a button, double click the button and and add the bellow code , and run your project :
2. Build and Run your Windows Form to consume the service








